
Chlorine will form at the positive electrode because non-metals form there from negatively charged non-metal ions. The cathode and anode terms are consistent with their redox reaction definitions in that reduction is subsequently occurring at the cathode and oxidation is occurring at the anode: Figure 5.5.1: Anode and cathode. Predict the products of electrolysis of molten calcium chloride.Ĭalcium will form at the negative electrode because metals form there from positively charged metal ions. Inside a device or cell, positively charged cations always migrate towards the cathode and negatively charged anions towards the anode, but the polarity of the. Lead and bromine form during the electrolysis of molten lead bromide A cathode and an anode are the two electrodes found in a battery or an electrochemical cell, which facilitate the flow of electric charge. So lead forms at the negative electrode and bromine forms at the positive electrode. The cathode is the positive or oxidizing electrode that acquires electrons from the external circuit. Depending upon the type of chemical reaction that occurs in an electrochemical cell, electrodes are classified into two types, namely cathode, and anode.The cathode and. Br - ions lose electrons at the anode and become Br atoms, which pair up to form Br 2 molecules.Pb 2+ ions gain electrons at the cathode and become Pb atoms.Molten lead bromide, PbBr 2 (l), is an electrolyte. anions lose electrons at the positively charged anode (The anode side has a base negative charge at the junction, since it supplied holes to the recombinant region and the doped ions have one electron more than.cations gain electrons from the negatively charged cathode.In any electric circuit, current flows from the. The negative end of the x-ray tube is called the cathode, and the positive end is called the anode. The x-ray tube consists of a cathode and an anode within a vacuum. As a result, they form atoms or molecules of elements: The x-ray tube is essentially a massive valve, or switch, completing an electric circuit. When ions reach an electrode, they gain or lose electrons. Ions migrate (move) towards their oppositely charged electrode Products of electrolysis Negatively charged ions are called anions. The positively charged electrode in electrolysis is called the anode. The electrolyte is a chemical medium that allows the flow of electrical charge between the cathode and anode. Positively charged ions are called cations. The negatively charged electrode in electrolysis is called the cathode.
#CATHODE AND ANODE CHARGE FREE#
The free ions in electrolytes are attracted to the oppositely-charged electrodes connected to the dc supply. Under these conditions, the ions in electrolytes are free to move within the liquid.Įlectrolysis is a process in which electrical energy, from a direct current (dc) supply, decomposes (breaks down) electrolytes. But for an electrolytic cell, the reverse is true.Electrolytes are ionic compounds that are either: So next time you need to know which is the anode and which is the cathode, remember not to PANIC!
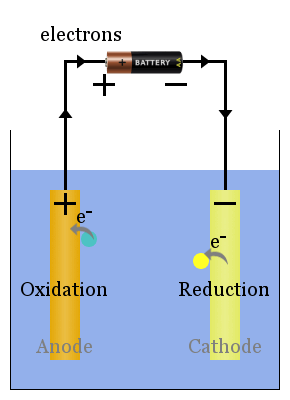
To remember which is which, just remember this: don'tįor which the first letters are as follows: You might think the anode attract positive ions and is negative, but that would be wrong - that is the cathode. Many people get confused between the anode and the cathode, and what they attract. Since it is positive, it will attract negative ions towards it. Both galvanic and electrolytic cells will consist of two electrodes (an anode and a cathode), which can be made of the same or different metals, and an.
#CATHODE AND ANODE CHARGE HOW TO#
How To Remember The Anode And Cathode Charge Education : ChemistryĪn anode is the electrode used in electrolysis which carries the positive charge in a solution. Demonstration of Faradion’s SIBs: (a) charge/discharge profiles of Faradion’s second-generation cathode material cycled in half-cells at C/5 within different voltage windows (b) the fast-charge performance of Faradion’s second-generation cathode materialHC 0.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
